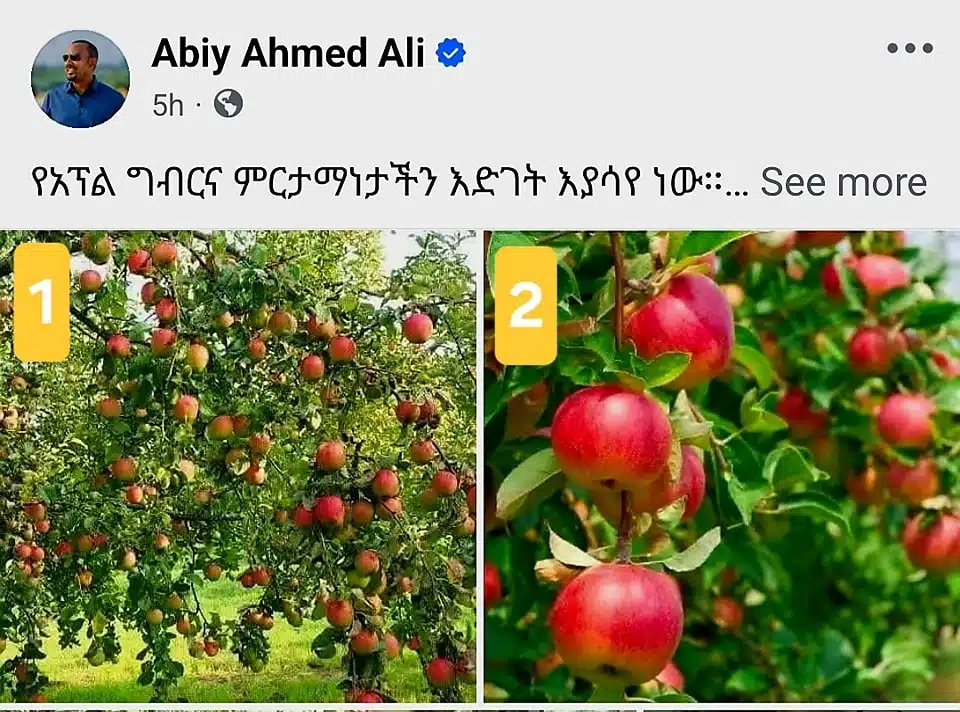
 In an era where social media shapes public opinion, ensuring accurate information is tantamount. A recent instance involving Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed’s Facebook and Twitter accounts flirts dangerously with misinformation. Six pictures depicting burgeoning apple orchards were posted with a proud claim, “Our Apple Agriculture is Growing.” However, do these picturesque images actually portray Ethiopia’s apple production? Ethiopia Check’s investigation unearths startling details suggesting otherwise. This article embarks on a comprehensive journey, scrutinizing the actual origin of these images while emphasizing the need for transparency, particularly when dealing with information shared on high-profile public platforms. Stay tuned to know if the apple trees depicted are really blossoming in Ethiopian soil or if they are just images cherry-picked from the worldwide web.
In an era where social media shapes public opinion, ensuring accurate information is tantamount. A recent instance involving Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed’s Facebook and Twitter accounts flirts dangerously with misinformation. Six pictures depicting burgeoning apple orchards were posted with a proud claim, “Our Apple Agriculture is Growing.” However, do these picturesque images actually portray Ethiopia’s apple production? Ethiopia Check’s investigation unearths startling details suggesting otherwise. This article embarks on a comprehensive journey, scrutinizing the actual origin of these images while emphasizing the need for transparency, particularly when dealing with information shared on high-profile public platforms. Stay tuned to know if the apple trees depicted are really blossoming in Ethiopian soil or if they are just images cherry-picked from the worldwide web.
Overview of the Situation
Introduction to the Prime Minister’s Apple Images
Images speak louder than words, and thus have the power to influence public perception significantly. Considering this potential, yesterday’s incident involving Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed’s social media accounts raised eyebrows. In a post evidently celebrating the country’s agricultural production, six apple images were shared with the caption: “Our Apple Agriculture is Growing.” Unfortunately, not everything was as it seemed.
These particular apple images, while representing lush, thriving apple agriculture, were in actuality not originating from Ethiopia. As an instant online search reveals, these images have been sourced from diverse websites, highlighting apple varieties grown outside of Ethiopia.
Objective of the Fact-Checking
Against the backdrop of this unfolding scenario, Ethiopia Check undertook a detailed fact-check to examine the authenticity of the apple images which were presented as symbols of Ethiopian apple agriculture. This exercise aimed to clarify the true origins of the disputed images and to assess whether they genuinely represented Ethiopian apple farming.
Fact-checking is not just about debunking single instances of misinformation but is an essential tool to maintain the integrity of public discourse – a necessity in our current digital age. The importance of accurate representation, especially in messages shared by public figures and institutions, cannot be overstated and this incident serves as an illustrative example of the same.
Analysis of the Images
In this section, we will scrutinize the origin of different images shared by Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed on his social media platforms and contrast them with Ethiopia’s apple agriculture.
Image Sources and Verification
Our ground-breaking look into the matter has discovered discrepancies that raise suspicions regarding the trustworthiness of these posts.
Source of Image 1
Upon mapping the digital footprint of the first image shared, it was discovered that this image depicts a ‘Cortland Apple Tree’: a variety that is chiefly grown in the United States. The image in question could be traced back to an online e-commerce website that offers these trees for sale here.
Source of Image 2
Similar to the aforementioned case, the image denoted as Image 2 is identified as a representation of an apple product known as ‘Malus Sap’, derived from Latin terminology. This product is also available online at an ecommerce site.
Comparing Images with Ethiopian Apple Products
With the dubious origins of the images released by the Prime Minister, we are posed with the question of the authenticity of these images in representing Ethiopian apple agriculture.
Lack of Ethiopian Apple Representation
Historically, Ethiopia has been known to grow apples, particularly in areas such as Central Ethiopia, East Gojam, and Gamo Zones. These areas harbor suitable climates and soil conducive for apple farming. However, the images used by the Prime Minister do not seem to correspond to the apple products that are generally cultivated in these regions.
Identification of Original Image Locations
Further, the other images shared possess urls from three different websites, suggesting that the images were not originally sourced from Ethiopia. These images, instead, belong to commercial databases from other regions. As discerning citizens and consumers of media, it is pertinent to be aware of the origins and authenticity of the content shared with us. Unverified content has the potential to misinform and misdirect public opinion—a risk that our community cannot afford to take.
The Importance of Image Authenticity
The degree of authenticity related to images shared on the internet, particularly on social media platforms, has an immense influence on the perception of the audience. The Prime Minister’s false claims regarding the images of Apple products can have a profound impact on people following him diligently. Such authenticity issues often lead to false impressions and assumptions, creating an illusion that might not be completely accurate.
Impact of Sharing Misleading Images
When influential figures like the Prime Minister share misleading images, it can further propel the spread of false information. In this particular case, the erroneous representation of Ethiopian Apple products can lead to widespread misconceptions about the advancement of Apple agriculture in the country. This could possibly affect the credibility of the Ethiopian government and could deter potential investments in the agricultural sector. Societal trust, once breached, may take a significant amount of time to restore. It creates a cascading effect, contributing to the overall ‘fake news’ crisis affecting our digital age.
Role of Authorities in Verifying Information
Authorities, including governmental bodies, regulatory agencies, media houses, and tech companies, have a pivotal role in verifying the information reaching the public.
Firstly, the government, especially its leaders, must maintain the highest standards of truthfulness, not only in their official releases but also on their social media platforms. For example, Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed, while promoting Ethiopian Apple products, should ensure that he uses authentic images from his country.
Furthermore, social media giants need to proactively use their technology and resources to spot and systematically debunk false information circulating on their platforms. These entities should collaborate more extensively with fact-checking organizations like Ethiopia Check, to timely identify, flag, and remove misleading content.
Lastly, the citizens themselves must be empowered to critically analyze the information they interact with. Public education campaigns on media literacy should be prioritized to equip the general public with skills to distinguish between genuine and manipulated content.
In summary, image authenticity is not just about presenting the truth. It is a crucial pillar holding up the integrity of communication, especially in the digital realm. When this is compromised, particularly by influential figures, it disruptively impacts public trust and perception. Therefore, all stakeholders, from authorities to individuals, must play their part in ensuring truth and transparency prevail in our shared digital space.
Preventing the Spread of False Information
In the digital age, the spread of misleading or downright false information is facilitated by the press of a button. It could involve manipulated media, like the images we discussed earlier, to propagate the wrong perception. Understanding and preventing the spread of such content is a tremendous responsibility that falls upon individuals, institutions, and authorities alike.
Efforts Required from Institutions and Individuals
Rather than passively consuming information, individuals must actively question the authenticity of what they see, read, or hear. Embracing skepticism could indeed be the first step towards curtailing the proliferation of fabricated content. However, being a responsible citizen in the digital world also means fact-checking before sharing, and discouraging others from spreading unverified information.
For institutions, the responsibility multiplies. Taking accountability for the content they share is essential. Institutions should establish stringent protocols for information validation before dissemination, particularly through social media channels where false information can spread like wildfire.
The role of educational institutions cannot be overstated in this regard. They should emphasize media literacy in their curriculums to foster a generation capable of distinguishing fake content from credible information.
Tools and Methods for Fact-Checking
Given the extent and speed of information spread, manually verifying everything is nearly impossible. Thus, utilizing technological advances is crucial for fact-checking. A multitude of tools and platforms such as Snopes, FactCheck.org, and Google’s Fact Check Explorer are available to verify a piece of information.
Reverse Image Search is another powerful tool, especially in our case of identifying the true source of an image. By uploading an image to a search engine like Google, one can discover its origin or other instances where it has been published.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning technologies have made strides in this arena too. They can process vast amounts of data, identify patterns and detect inconsistencies, thus providing a robust framework for fact-checking.
One can also resort to various online tutorials and guidelines on using these resources for verifying information. Thus, the amalgamation of human initiative and technological means plays a significant role in fact-checking, effectively debunking false narratives and preventing the spread of baseless information.





